JavaFX绑定同步两个值:当因变量更改时,其他变量更改。
要将属性绑定到另一个属性,请调用bind()方法,该方法在一个方向绑定值。例如,当属性A绑定到属性B时,属性B的更改将更新属性A,但不是相反。
JavaFX提供了许多绑定选项,以便在域对象和GUI控件中的属性之间进行同步。
我们可以在JavaFX的属性API中使用以下三种绑定策略:
双向绑定绑定相同类型的属性,并同步两侧的a值。
当与bindBidirectional()方法双向绑定时,需要两个属性都必须是可读/可写的。
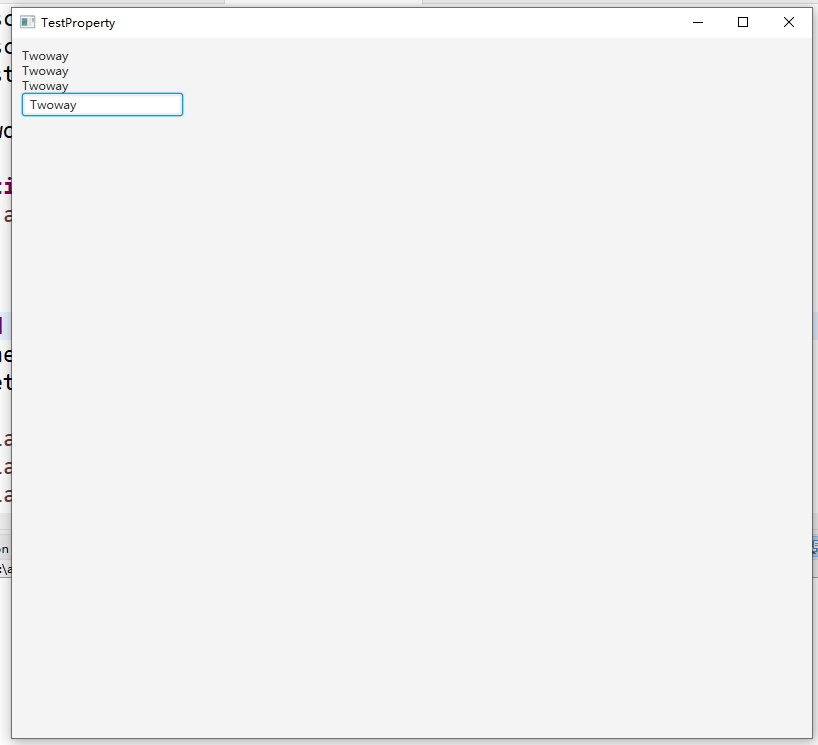
以下为一个双向绑定的示例,将三个 Label 的 textProperty 与 TextField 的 textProperty 进行双向绑定,则当TextField的值发生改变的时候,三个 Label 的显示内容也相应地发生改变。
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.beans.property.StringProperty;
import javafx.geometry.Insets;
import javafx.geometry.Orientation;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.control.Label;
import javafx.scene.control.TextField;
import javafx.scene.layout.FlowPane;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
public class TwowayBindProperty extends Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
launch(args);
}
@Override
public void start(Stage primaryStage) throws Exception {
FlowPane pane = new FlowPane(Orientation.VERTICAL);
pane.setPadding(new Insets(10));
Label label1 = new Label();
Label label2 = new Label();
Label label3 = new Label();
TextField textField = new TextField();
pane.getChildren().add(label1);
pane.getChildren().add(label2);
pane.getChildren().add(label3);
pane.getChildren().add(textField);
StringProperty textProperty = textField.textProperty();
textProperty.bindBidirectional(label1.textProperty());
textProperty.bindBidirectional(label2.textProperty());
textProperty.bindBidirectional(label3.textProperty());
Scene scene = new Scene(pane, 800, 700);
primaryStage.setScene(scene);
primaryStage.setTitle("TestProperty");
primaryStage.show();
}
}
我们还可以使用JavaFX Fluent API来绑定属性, Fluent API在各种依赖对象上暴露方法。
JavaFX Fluent API 提供的方法常用的有 multiply(),divide(),subtract(),isEqualTo(),isNotEqualTo(),concat()等。请注意,方法名称中没有get或set。使用的时候,使用链式调用的方式,例如: width().multiply(height()).divide(2)。
如下示例,展示了怎样使用JavaFX Fluent API高级绑定来计算一个矩形的面积。按照上述,择代码如下:
import javafx.beans.binding.NumberBinding;
import javafx.beans.property.IntegerProperty;
import javafx.beans.property.SimpleIntegerProperty;
public class FluentProperty {
public static void main(String[] args) {
IntegerProperty width = new SimpleIntegerProperty(5); // 宽
IntegerProperty height = new SimpleIntegerProperty(2); // 高
NumberBinding area = width.multiply(height); //面积为宽乘高
System.out.println(area.getValue());//10
width.set(2); //将宽重设为 2
System.out.println(area.getValue());//4, 说明绑定有效
}
}
当对 NumberBinding 类进行子类化时,我们使用低级绑定,例如Double类型的DoubleBinding类。
在DoubleBinding类的子类中,我们重写其 computeValue()方法,以便我们可以使用运算符(如* 和 - )来进行复杂的运算。
高级绑定使用诸如multiply(),subtract()等方法, 低级绑定使用诸如*和 - 之类的运算符。
以下代码将上面高级绑定计算矩形面积改写为使用低级绑定的方式计算矩形面积。
import javafx.beans.binding.DoubleBinding;
import javafx.beans.property.DoubleProperty;
import javafx.beans.property.SimpleDoubleProperty;
public class LowProperty {
public static void main(String[] args) {
DoubleProperty width = new SimpleDoubleProperty(5.0); // 宽
DoubleProperty height = new SimpleDoubleProperty(2.0); // 高
DoubleBinding area = new DoubleBinding () {
{
super.bind(width, height);
}
@Override
protected double computeValue() {
return width.get() * height.get(); //面积为宽乘高
}
};
System.out.println(area.getValue());//10
width.set(2); //将宽重设为 2
System.out.println(area.getValue());//4, 说明绑定有效
}
}